Comparing Health Insurance in US, Europe, and Asia: A Comprehensive Analysis
Embarking on the journey of Comparing Health Insurance in US, Europe, and Asia, this introduction aims to provide a captivating glimpse into the intricate world of healthcare systems across different regions.
The following section delves into the nuances of health insurance structures in the US, Europe, and Asia, highlighting key differences and stakeholders involved.
Overview of Health Insurance Systems
In the United States, health insurance is primarily provided through employer-sponsored plans, government programs like Medicare and Medicaid, and individual marketplaces. The system is a mix of public and private insurance, with a significant portion of the population uninsured.In Europe, most countries have universal healthcare systems funded through taxation, providing coverage to all residents.
Private insurance can also supplement these public systems, offering additional benefits and faster access to care.In Asia, health insurance systems vary widely across countries. Some countries have national health insurance schemes, while others rely more on private insurance or out-of-pocket payments.
The accessibility and quality of healthcare services can also differ significantly.
Structural Differences
- In the US, health insurance is often tied to employment, with individuals purchasing plans independently if not covered by employers or government programs.
- European countries typically have a single-payer system or a combination of public and private insurance, ensuring universal coverage for all residents.
- Asia showcases a diverse range of insurance models, from government-run schemes to private insurance companies dominating the market in some countries.
Key Stakeholders
- United States:Employers, insurance companies, government agencies (such as CMS), healthcare providers, and individuals are major stakeholders in the US health insurance system.
- Europe:Governments, healthcare providers, insurance companies, and citizens play crucial roles in the European health insurance systems, with a focus on equitable access to care.
- Asia:Key stakeholders in Asian health insurance systems include government bodies, private insurers, healthcare providers, employers, and individuals, with varying degrees of government involvement depending on the country.
Coverage and Benefits
In terms of coverage and benefits, health insurance plans in the US, Europe, and Asia offer a range of options tailored to the specific needs of their populations.
Types of Coverage
In the US, health insurance plans typically cover essential health benefits mandated by the Affordable Care Act, including hospitalization, prescription drugs, preventive care, and maternity care. Employers often provide health insurance as part of their benefits package.In Europe, many countries have universal healthcare systems that provide coverage for all residents, regardless of employment status.
These systems often cover a wide range of services, including doctor visits, hospitalization, mental health services, and long-term care.In Asia, health insurance coverage varies widely depending on the country. Some countries have universal healthcare systems, while others rely more on private insurance.
Coverage may include outpatient services, hospitalization, and specialist care.
Standard Benefits
Standard health insurance packages in the US typically include coverage for primary care visits, emergency care, prescription drugs, and preventive services. Deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance are common features of these plans.In Europe, standard benefits often include access to primary care physicians, specialists, hospital services, and preventive care.
Many countries also cover dental care, vision care, and mental health services as part of their basic benefits package.In Asia, standard benefits can vary widely depending on the country and type of insurance plan. Some plans may cover a wide range of services, while others may be more limited in scope.
Dental care, vision care, and maternity care are commonly included in health insurance packages.
Unique Coverage Options
In the US, some health insurance plans offer telemedicine services, allowing patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely. Wellness programs, such as gym memberships and smoking cessation programs, are also common benefits offered by some plans.In Europe, many countries provide coverage for alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and chiropractic care, as part of their health insurance plans.
Some countries also offer coverage for medical tourism, allowing patients to receive treatment in other countries.In Asia, some health insurance plans offer coverage for traditional medicine practices, such as Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine. Long-term care benefits, including coverage for nursing homes and home healthcare services, are also available in some countries.
Cost and Affordability
In examining the cost and affordability of health insurance in the US, Europe, and Asia, it is crucial to consider various factors that influence the accessibility of healthcare services in each region.
Health Insurance Premiums
In the United States, health insurance premiums can vary significantly depending on factors such as age, location, and coverage levels. Premiums tend to be higher compared to Europe and Asia due to the complex healthcare system and the higher cost of medical services.
In Europe, health insurance premiums are often lower as many countries have universal healthcare systems funded through taxes. Asian countries also offer a mix of public and private insurance options with varying premium costs.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses and Co-payments
In the US, individuals are often required to pay high out-of-pocket expenses and co-payments for medical services, even with insurance coverage. This can lead to financial strain for many individuals, especially those with chronic illnesses or pre-existing conditions. In Europe, out-of-pocket expenses and co-payments are typically lower or non-existent in countries with universal healthcare systems.
In Asia, the out-of-pocket costs can vary depending on the type of insurance coverage and the healthcare provider.
Affordability for the General Population
Health insurance affordability remains a significant issue in the US, where many individuals struggle to afford coverage due to high premiums and out-of-pocket costs. This has led to a significant portion of the population being uninsured or underinsured. In Europe, the general population benefits from universal healthcare systems that provide affordable coverage for all residents.
In Asia, affordability varies across countries, with some nations offering more affordable insurance options compared to others.
Accessibility and Quality of Care
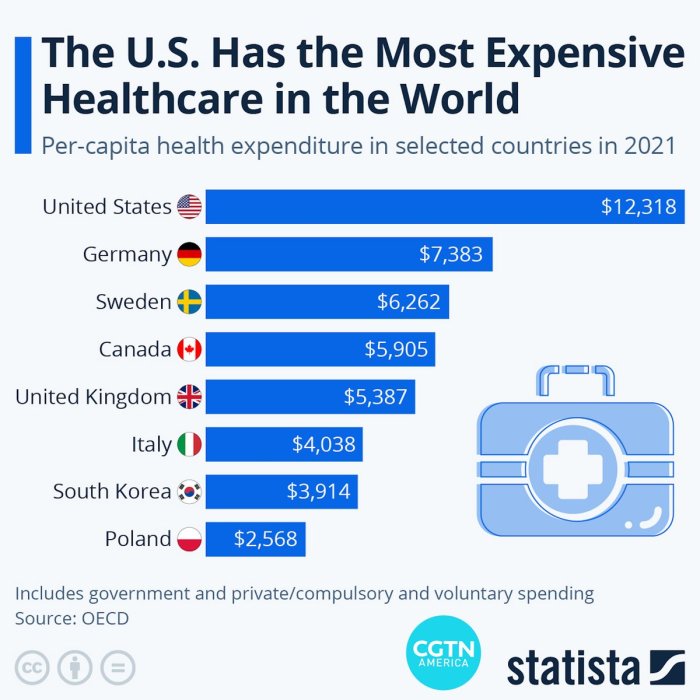
In evaluating the accessibility and quality of healthcare services provided through health insurance in the US, Europe, and Asia, it is important to consider the differences in healthcare systems and resources available in each region.
Accessibility of Healthcare Services
- In the United States, access to healthcare services through health insurance can be challenging for many individuals due to high premiums, deductibles, and co-pays. This can result in delayed or limited access to necessary medical care.
- European countries, on the other hand, generally have universal healthcare systems that provide more affordable access to a wide range of medical services. Patients often have the freedom to choose their healthcare providers without financial barriers.
- In Asia, access to healthcare services through health insurance varies widely depending on the country. Some countries have robust public healthcare systems that provide affordable care, while others may have more limited coverage and higher out-of-pocket costs for patients.
Quality of Care Provided
- Health insurance plans in the US often provide access to state-of-the-art facilities, advanced medical technology, and highly skilled medical professionals. However, the quality of care can be influenced by the patient's ability to afford higher-tier plans.
- European health insurance plans prioritize providing high-quality care to all residents, regardless of their socio-economic status. This includes access to modern facilities, cutting-edge medical technology, and well-trained healthcare professionals.
- In Asia, the quality of care provided under health insurance plans can vary significantly between countries. Some countries may have world-class medical facilities and expertise, while others may struggle to provide adequate care due to resource limitations.
Disparities in Healthcare Access
- In the US, disparities in healthcare access and quality often exist along socio-economic lines. Lower-income individuals may face greater barriers to accessing quality care compared to those with higher incomes, leading to inequalities in health outcomes.
- Europe has made efforts to reduce disparities in healthcare access by implementing universal healthcare systems that aim to provide equal access to all residents. However, disparities may still exist based on factors such as geographical location or language barriers.
- In Asia, socio-economic disparities can significantly impact access to quality healthcare services. Wealthier individuals may have access to top-tier medical facilities and experts, while lower-income individuals may struggle to afford basic healthcare services.
Last Word
Concluding our exploration of health insurance systems in the US, Europe, and Asia, this summary encapsulates the essential points discussed, offering a holistic view of the topic.
Clarifying Questions
What are the major differences in health insurance systems between the US, Europe, and Asia?
The US follows a predominantly private insurance model, while Europe relies more on public and social insurance systems. Asia showcases a mix of private and public insurance schemes.
Are there any unique coverage options specific to each region?
Yes, for example, Europe often includes coverage for maternity care as a standard benefit, which might not be as prevalent in the US or Asia.
How do out-of-pocket expenses compare in the US, Europe, and Asia?
Out-of-pocket expenses are generally higher in the US compared to Europe and Asia due to the more privatized nature of the healthcare system.
What disparities exist in healthcare access among different socio-economic groups in these regions?
In the US, socio-economic disparities are more pronounced due to the lack of universal healthcare, while Europe and Asia tend to have more equitable access based on social insurance models.



